Phlebotomy Techniques and Their Impact on Health Outcomes: Is Phlebotomy Public Health Or Health Science
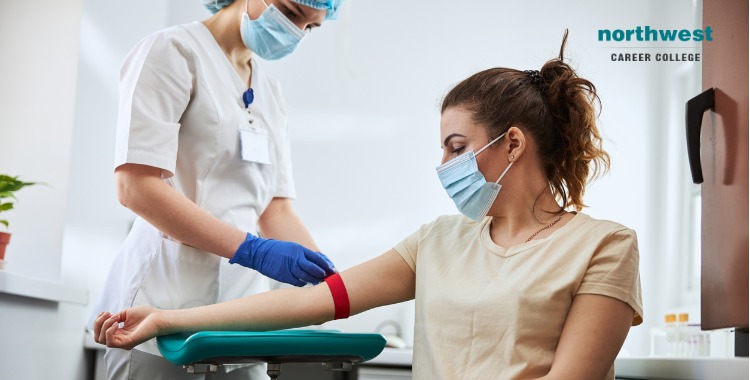
Phlebotomy, the process of drawing blood from a vein, is a fundamental procedure in healthcare. The technique employed significantly impacts both patient safety and the quality of the collected sample, ultimately influencing the accuracy of diagnostic tests and the effectiveness of treatment. Different techniques exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages concerning patient comfort, risk of complications, and sample integrity.
Is phlebotomy public health or health science – Proper phlebotomy technique is crucial for ensuring accurate and reliable laboratory results. Inaccurate techniques can lead to hemolysis (rupture of red blood cells), clotting, or contamination of the sample, all of which can compromise the validity of the test results. Conversely, meticulous technique contributes to patient satisfaction and minimizes the risk of complications.
Comparison of Phlebotomy Techniques and Their Effect on Patient Safety
Several methods exist for venipuncture, including vacuum tube collection, syringe method, and butterfly needle collection. Vacuum tube systems are widely used for their efficiency and ease of use. However, improper insertion or excessive vacuum pressure can cause hematoma formation (blood clotting under the skin) or nerve damage. The syringe method offers greater control over blood flow, which is beneficial for patients with fragile veins or difficult venipuncture sites. However, it is more time-consuming. Butterfly needles, ideal for patients with small or fragile veins, minimize the risk of hematoma formation but may require more expertise to use effectively. The choice of technique depends on the patient’s individual circumstances and the phlebotomist’s skill. Ultimately, adhering to established protocols and employing the most appropriate technique for each patient significantly reduces the risk of complications.
The Importance of Proper Venipuncture Technique in Preventing Healthcare-Associated Infections
Proper venipuncture technique plays a vital role in preventing healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). Failing to adhere to aseptic techniques, such as inadequate hand hygiene, improper use of gloves, or contamination of equipment, can introduce pathogens into the bloodstream, leading to serious infections like bacteremia or septicemia. Strict adherence to infection control protocols, including the use of sterile equipment, proper antiseptic skin preparation, and correct disposal of sharps, is paramount in minimizing the risk of HAIs associated with phlebotomy. For example, failing to properly disinfect the venipuncture site before insertion can lead to the introduction of skin flora into the bloodstream.
Best Practices for Minimizing Patient Discomfort During Phlebotomy Procedures
Patient comfort is a key consideration in phlebotomy. Several strategies can minimize discomfort during the procedure. These include selecting appropriate vein sites, using smaller gauge needles when possible, applying proper tourniquet pressure, inserting the needle smoothly and quickly, and avoiding repeated needle sticks. Effective communication with the patient, explaining the procedure and providing reassurance, can also significantly reduce anxiety and discomfort. Post-procedure care, such as applying pressure to the venipuncture site to prevent hematoma formation and providing a bandage, further enhances patient comfort and minimizes the risk of complications. A calm and professional demeanor from the phlebotomist is essential for a positive patient experience.
Steps Involved in a Standard Venipuncture Procedure
Proper preparation and execution of a venipuncture procedure are essential to minimize complications and ensure the quality of the blood sample. The following steps Artikel a standard procedure:
- Verify patient identity and confirm the test orders.
- Explain the procedure to the patient and obtain informed consent.
- Perform hand hygiene and don gloves.
- Select an appropriate vein and apply a tourniquet.
- Prepare the venipuncture site with antiseptic solution.
- Insert the needle into the vein at the appropriate angle.
- Collect blood samples into the appropriate tubes.
- Remove the tourniquet and needle, applying pressure to the site.
- Label the tubes with the patient’s information.
- Dispose of sharps and other waste appropriately.
- Provide post-procedure care and instructions to the patient.
Phlebotomy’s Place within the Healthcare System
Phlebotomy, while often considered a foundational procedure, plays a crucial and multifaceted role within the broader healthcare system. Its integration spans various settings, impacting both individual patient care and broader public health initiatives. The accuracy and efficiency of phlebotomy directly influence the quality of diagnostic testing and treatment efficacy, making it an indispensable component of modern healthcare delivery.
Phlebotomists are highly skilled professionals whose work significantly impacts patient care and healthcare research. Their contributions are not limited to the technical aspects of blood collection; they also encompass patient interaction, adherence to safety protocols, and the accurate handling of samples that are crucial for reliable results.
Phlebotomy Services in Different Healthcare Settings
Phlebotomy services are integrated into a variety of healthcare settings, each with its unique operational requirements and demands. In hospitals, phlebotomists are often part of a larger laboratory team, working collaboratively with nurses, doctors, and other healthcare professionals to collect samples for a wide range of tests, from routine blood counts to complex diagnostic procedures. The volume of samples collected in a hospital environment is typically high, demanding efficiency and meticulous attention to detail. In contrast, clinics may have a smaller phlebotomy team, focusing on a more limited range of tests tailored to the clinic’s specialty. The patient interactions in a clinic setting may be more extended, allowing for greater patient education and reassurance. Blood banks rely heavily on skilled phlebotomists to collect donations, maintaining strict adherence to safety protocols and ensuring the quality and integrity of the blood supply. The focus here is on efficient and safe blood collection, as well as donor management and record-keeping.
Roles and Responsibilities of Phlebotomists
The core responsibilities of a phlebotomist are consistent across different healthcare environments: accurate and safe blood collection, proper labeling and handling of specimens, and maintaining detailed records. However, the specific tasks and responsibilities can vary depending on the setting. In hospitals, phlebotomists may perform a wider range of procedures, including arterial punctures, and handle a greater variety of sample types. In clinics, they may be more involved in patient education and communication, explaining procedures and addressing patient concerns. In blood banks, their responsibilities heavily emphasize donor safety and adherence to strict regulatory guidelines. Across all settings, effective communication and interpersonal skills are crucial, as phlebotomists are often the first point of contact for patients undergoing blood collection. Maintaining confidentiality and adherence to patient privacy regulations is also paramount.
Phlebotomy’s Contribution to Health Science Research and Public Health
Phlebotomy plays a vital role in both health science research and public health initiatives. In research, blood samples collected by phlebotomists provide crucial data for various studies, from investigating disease mechanisms to evaluating the efficacy of new treatments. The quality and accuracy of the samples collected directly influence the reliability of research findings. In public health, phlebotomy is essential for population-based screening programs, such as newborn screening, blood donation drives, and epidemiological studies. Data obtained from these programs contribute significantly to disease surveillance, informing public health policies and resource allocation.
Phlebotomy Data and Population Health, Is phlebotomy public health or health science
Phlebotomy data contributes significantly to the overall health of a population by providing insights into disease prevalence, risk factors, and treatment outcomes. For instance, data from routine blood tests can identify early signs of diseases like diabetes or heart disease, enabling timely intervention and improving patient outcomes. Epidemiological studies using phlebotomy data can identify trends in disease incidence and prevalence, helping public health officials to design effective prevention and control strategies. Population-level data on blood types and other blood markers can also inform blood supply management and ensure sufficient resources are available for transfusion needs. The accuracy and completeness of phlebotomy data are critical for reliable epidemiological modeling and effective public health interventions. For example, tracking blood lead levels in children through widespread phlebotomy-based screening programs allows for early identification of environmental hazards and implementation of targeted interventions to reduce lead exposure.

Tim Redaksi